
Just because the bulbs are shaped similarly, doesn’t mean they share many traits.
The original automobiles literally used lamps (glass housing with a candle burning inside) to light the way on the roads, similar to how people would light the way on horseback. And I’m sure you’ve heard of Thomas Edison, who invented the first long-lasting incandescent light bulb in 1879, what most vehicles use in their modern day headlamps are based off of his original designs. A standard light bulb has a filament, and it gets electricity applied to each side of the filament and when this happens the filament gets very hot and reaches a state of incandescence. This is why we call light bulbs with filaments, incandescent light bulbs. High-power incandescent light bulbs used in car headlights are filled with a gas called Halogen, and it reacts to the brightly glowing filament and creates a massive amount of light, up to 1,200 Lumen of light output. This is why we call standard automotive headlights “halogen bulbs”.
This is not to be confused with Xenon or HID bulbs – they don’t necessarily mean the same thing. An HID light bulb (stands for High Intensity Discharge) is filled with Xenon gas which reacts to the spark created inside the HID bulb. This xenon gas is ignited and creates a vast and powerful amount of light output that can be measured in thousands of Lumen, depending on the power consumption (normally 35w, 55w or 75w). Today, a vehicle that comes factory-equipped with xenon lighting uses a 35w lighting system.
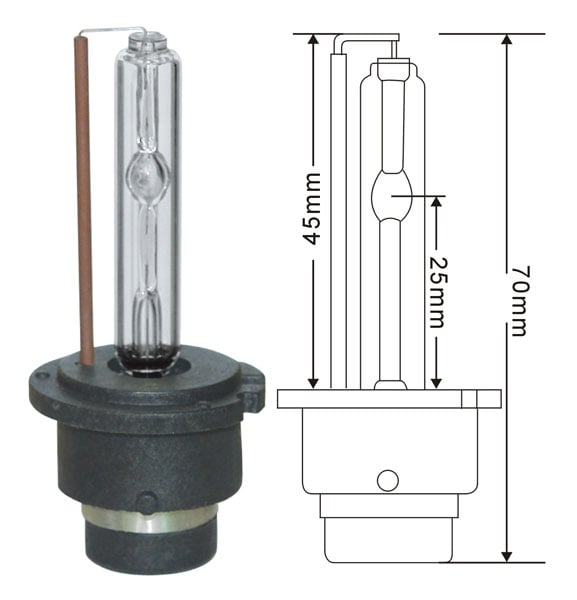
A Xenon HID bulb does not have a filament, instead it has two electrodes that meet inside the xenon-glass filled bulb. A ballast is used to send up to 24,000 volts of AC electricity that creates a powerful spark and ignites the xenon gas mixture. This process is sustained and produces the exuberant amount of light output:
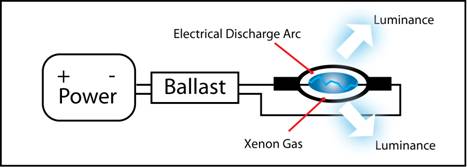
A true HID bulb uses a ballast to ignite the chemical mixture inside. It does not use a filament.
- Xenon is 300 times brighter than halogen
- Xenon can last 10 times longer than halogen
- Xenon produces cleaner, whiter, brighter and safer light
- A 35W Xenon bulb consumes less power than a 55W Halogen bulb
- Halogen bulbs burn hotter than the same wattage Xenon bulbs
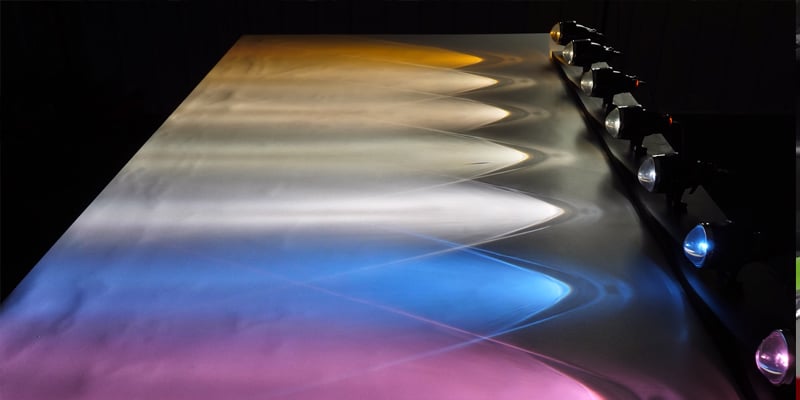
Upgrading your headlights from halogen bulbs to HID technology will make a huge difference in visibility at night by projecting a further beam of light and broadening your road coverage. You will see further, see more and be more visible to other drivers. The sooner you can see hazards on the road, the more time you have to react.
Halogen bulbs operate at 12V and use old lighting technology by heating a wire filament to emit light. Over a short period of time that wire filament becomes brittle, and small vibrations caused by everyday driving causes damage to the halogen filament affecting it’s light output and the bulb’s reliability.
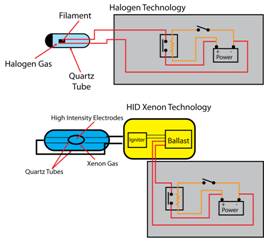
Difference between incandescent halogen light bulbs and HID xenon light bulbs.
Disclaimer:
Street legal in the USA for Fog Light use. Not compliant with DOT / FMVSS108 and not street legal in the USA for Headlights. Certain specialty vehicles strictly limited to off-street use and not having DOT registration or license plates may use these products exclusively off-streets. International street legality varies by country. Note: This usage regulation is not unique to any specific bulbs, ALL LED and HID bulbs from all other brands, regardless of marketing claims, are prohibited from street use in halogen headlights in the USA.




.png?width=300&height=87&name=logo%20(1).png)